Creating Active Datagaurd in 11g using RMAN backup restore(Manual restore standby)
This post is about the creation of Active Datagaurd in 11g using RMAN backup restore,there arevarious differenet methods of creating a standby database in oracle 11g for eg
1)-Using RMAN duplicate command
2)-Manual standby using the database files
3)-Using Backup Restore
i am using RMAN backup restore(Manual restore standby) in the post
Follow these simple steps for the creation of Active Datagaurd in 11g using RMAN backup restore(Manual restore standby) Screenshots are also provided for a better result
Step 1)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-check for archivelog mode,check that the primary server is in archivelog mode,if it is not in archivelog mode then convert it into archivelog mode
Step 3)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Check the setting for the DB_NAME and DB_UNIQUE_NAME parameters,this is helpful as you have to set the same values in the standby server
Step 4)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-add the name of standby database and the service name of the standby server in log_archive_config parameter,this can be used for sending redo logs to standby server
Step 5)_ON STANDBY SERVER-install only binaries in exact location as in PRIMARY
Step 6)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Set suitable remote archive log destinations and enable remote archiving,this can be done by using the service name for the standby database
Step 7)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-set archive log format,max process and password file exclusivity
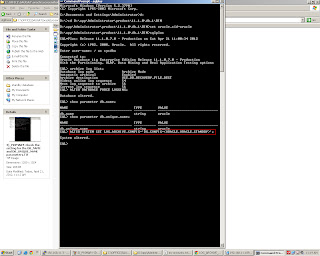
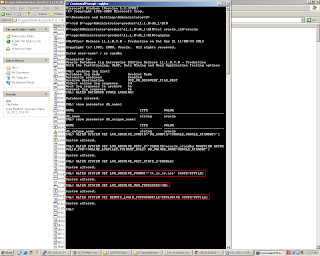
Step 8)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-it is recommended to make sure the primary is ready to switch roles to become a standby. For that we need to set these parameters
1)-FAL_SERVER
2)-DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT
3)-LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT
Step 9)_ON PRIMARY AND STANDBY SERVER-Entries for the primary and standby databases are needed in the tnsnames.ora files on both servers
Step 10)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-take a backup of the primary database,this step distinguishes this type of method creating the standby database,if you are using RMAN DUPLICATE command then this step is not necessary
Step 11)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Create a controlfile for the standby database
Step 12)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Create a parameter file for the standby database
Step 13)_ON STANDBY SERVER-make exact folders in the standby server as there in the primary server
Step 14)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-copy the newly created standby control file
Step 15)_ON STANDBY SERVER-paste the controlfile to the standby server and rename it to control01,02,03 respectively
Step 16)_ON STANDBY SERVER-copy and paste controlfile,archive log files,datafiles,password file,backupset into the standby server to the exact location as of the primary server
Step 17)_ON STANDBY SERVER-make changes in the tnsnames file for the standby server
Step 18)_ON STANDBY SERVER-start the listener
Step 19)_ON STANDBY SERVER-make the following changes in the standby server pfile
1)-FAL_SERVER
2)-LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2
3)-DB_UNIQUE_NAME
Step 20)_ON STANDBY SERVER-create a new service for the database using oradim
Step 21)_ON STANDBY SERVER-startup the server in nomount mode using the newly created pfile
Step 22)_ON STANDBY SERVER-create spfile from the standby server pfile
Step 23)_ON STANDBY SERVER-shutdown n startup in nomount using newly created spfile
Step 24)_ON STANDBY SERVER RMAN-mount the database and restore the database
Step 25)_ON STANDBY SERVER-create the online redo logs
Step 26)_ON STANDBY SERVER-In addition to the online redo logs, you should create standby redo logs on both the standby and the primary database (in case of switchovers)
Step 27)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-switch the logfile to see the archivelog generation and also check the copying it to standby
Step 28)_ON STANDBY SERVER-recover the standby to make it upto-date with primary
This post is about the creation of Active Datagaurd in 11g using RMAN backup restore,there arevarious differenet methods of creating a standby database in oracle 11g for eg
1)-Using RMAN duplicate command
2)-Manual standby using the database files
3)-Using Backup Restore
i am using RMAN backup restore(Manual restore standby) in the post
Follow these simple steps for the creation of Active Datagaurd in 11g using RMAN backup restore(Manual restore standby) Screenshots are also provided for a better result
Step 1)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-check for archivelog mode,check that the primary server is in archivelog mode,if it is not in archivelog mode then convert it into archivelog mode
Step 2)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Enabled forced logging so that everything gets logged
Step 4)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-add the name of standby database and the service name of the standby server in log_archive_config parameter,this can be used for sending redo logs to standby server
Step 5)_ON STANDBY SERVER-install only binaries in exact location as in PRIMARY
Step 6)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Set suitable remote archive log destinations and enable remote archiving,this can be done by using the service name for the standby database
Step 7)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-set archive log format,max process and password file exclusivity
Step 8)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-it is recommended to make sure the primary is ready to switch roles to become a standby. For that we need to set these parameters
1)-FAL_SERVER
2)-DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT
3)-LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT
Step 9)_ON PRIMARY AND STANDBY SERVER-Entries for the primary and standby databases are needed in the tnsnames.ora files on both servers
Step 10)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-take a backup of the primary database,this step distinguishes this type of method creating the standby database,if you are using RMAN DUPLICATE command then this step is not necessary
Step 11)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Create a controlfile for the standby database
Step 12)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-Create a parameter file for the standby database
Step 13)_ON STANDBY SERVER-make exact folders in the standby server as there in the primary server
Step 14)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-copy the newly created standby control file
Step 15)_ON STANDBY SERVER-paste the controlfile to the standby server and rename it to control01,02,03 respectively
Step 16)_ON STANDBY SERVER-copy and paste controlfile,archive log files,datafiles,password file,backupset into the standby server to the exact location as of the primary server
Step 17)_ON STANDBY SERVER-make changes in the tnsnames file for the standby server
Step 18)_ON STANDBY SERVER-start the listener
Step 19)_ON STANDBY SERVER-make the following changes in the standby server pfile
1)-FAL_SERVER
2)-LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2
3)-DB_UNIQUE_NAME
Step 20)_ON STANDBY SERVER-create a new service for the database using oradim
Step 21)_ON STANDBY SERVER-startup the server in nomount mode using the newly created pfile
Step 22)_ON STANDBY SERVER-create spfile from the standby server pfile
Step 23)_ON STANDBY SERVER-shutdown n startup in nomount using newly created spfile
Step 24)_ON STANDBY SERVER RMAN-mount the database and restore the database
Step 25)_ON STANDBY SERVER-create the online redo logs
Step 26)_ON STANDBY SERVER-In addition to the online redo logs, you should create standby redo logs on both the standby and the primary database (in case of switchovers)
Step 27)_ON PRIMARY SERVER-switch the logfile to see the archivelog generation and also check the copying it to standby
Step 28)_ON STANDBY SERVER-recover the standby to make it upto-date with primary
Congratulations!!!
You have successfully created an active datagaurd using RMAN restore command
_PRIMARY-check+for+archivelog+mode.TIF)
_PRIMARY-Enabled+forced+logging+so+that+everything+gets+logged.TIF)
_PRIMARY-Check+the+setting+for+the+DB_NAME+and+DB_UNIQUE_NAME+parameters.TIF)

_PRIMARY-it+is+recommended+to+make+sure+the+primary+is+ready+to+switch+roles+to+become+a+standby.+For+that+we+need+to+set+these+parameters.TIF)
_PRIMARY,STANDBY-Entries+for+the+primary+and+standby+databases+are+needed+in+the+tnsnames.ora+files+on+both+servers.TIF)
_PRIMARY-take+a+backup+of+the+primary+database.TIF)
_PRIMARY-Create+a+controlfile+for+the+standby+database.TIF)
_PRIMARY-Create+a+parameter+file+for+the+standby+database.TIF)
_STANDBY-make+exact+folders+in+the+standby+server.TIF)
_PRIMARY-copy+the+newly+created+standby+control+file.TIF)
_STANDBY-paste+the+controlfile+to+the+standby+server+and+rename+it+to+control01,02,03.TIF)
_STANDBY-copy+and+paste+controlfile,archive+log+files,datafiles,password+file,backupset+into+the+standby+server.TIF)
_STANDBY-make+changes+in+the+tnsnames+file.TIF)
_STANDBY-start+the+listener.TIF)
_STANDBY-make+the+following+changes+in+the+standby+server+pfile.TIF)
_STANDBY-create+a+new+service+for+the+database.TIF)
_STANDBY-startup+nomount+the+database+using+the+pfile.TIF)
_STANDBY-create+spfile+from+the+standby+server+pfile.TIF)
_STANDBY-shutdown+n+startup+in+nomount+using+newly+created+spfile.TIF)
_STANDBY-mount+the+database+and+restore+the+database.TIF)
_STANDBY-create+the+online+redo+logs.TIF)
_STANDBY-In+addition+to+the+online+redo+logs,+you+should+create+standby+redo+logs+on+both+the+standby+and+the+primary+database+(in+case+of+switchovers).TIF)
_PRIMARY-switch+the+logfile+to+see+the+archivelog+generation+and+also+check+the+copying+it+to+standby.TIF)
_STANDBY-recover+the+standby+to+make+it+upto-date+with+primary.TIF)
_configure+the+network+files.TIF)
_make+entries+for+source+and+target+database+into+the+listener+file(preferably+through+net+manager)+and+restart+the+listener+afterwards.TIF)
_make+entry+for+the+target+database+in+the+tnsnames+file.TIF)
_place+this+parameter+in+the+tnsnames+file+to+avoid+connection+blocking+error+generated+from+listener.TIF)
_create+a+new+instance+for+the+new+target+database.TIF)
_create+a+password+file+with+a+password+for+the+target+database+format+for+the+same+would+be+PWDinstancename.ora.TIF)
_connect+with+the+source+database+and+create+a+pfile+from+spfile.TIF)
_make+the+following+changes+in+the+newly+created+pfile(left+one+is+of+source+db+and+right+one+is+created+for+clone+db).TIF)
_create+appropriate+folder+for+adump.TIF)
_create+appropriate+folder+for+clonedb+files+in+oradata+folder.TIF)
_set+oracle+sid+for+clone+db+and+connect+and+start+it+with+newly+created+pfile.TIF)
_now+create+the+spfile+from+the+newly+created+pfile+and+then+shu+n+start+the+db+again.TIF)
_connect+with+the+rman+of+source+database+with+user+sys+and+the+password+for+sys(not+like+rman+target+slash).TIF)
_connect+with+the+auxiliarry+clone+database+with+the+password+for+the+sys+user.TIF)
_perform+the+cloning+of+the+database+using+the+following+command.TIF)
_connect+with+the+clone+db+and+check+for+the+working+status+as+well+as+total+objects.TIF)
+connect+to+the+database+and+connect+to+particular+user+in+database+whose+query+is+to+be+tuned.TIF)
+now+fire+the+query+which+is+taking+time+or+sql+query+which+you+want+to+tune..TIF)
+use+autotrace+utility+by+making+traceonly+option+and+again+fire+the+query+which+you+want+to+tune.TIF)
+now+from+execution+plan+you+can+check+consisten+gets,+physical+reads,+sorts+to+disk,+recursive+calls+and+sorts+to+memory+and+fine+tune+your+query+based+on+this.TIF)
_grant+advisor+privilege+to+scott+and+connect+with+it.TIF)
_run+the+procedure+with+case+sensetive+username.TIF)
_execute+the+newly+created+tuning+task.TIF)
_Once+the+tuning+task+has+executed+successfully+the+recommendations+can+be+displayed+using+the+REPORT_TUNING_TASK+function..TIF)
_you+can+check+the+status+of+the+tuning+task+with+dba_advisor_log+view.TIF)
_Once+the+tuning+session+is+over+the+tuning+task+can+be+dropped+using+the+DROP_TUNING_TASK+procedure..TIF)